Magnetic Resonance Imaging

How it came to be
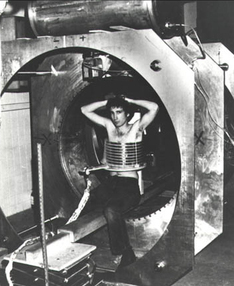
As Dr. Raymond Damadian witnessed the unfortunate death of his grandmother to cancer, he knew he wanted to invent something to assist in the diagnosis of these detrimental disease. As he started his research, he saw that cancer cells had a longer T1 and T2 value than normal cells. It was in 1972, he filed for an US patent for a method to detect cancerous cells. He decided that he and his team would build a machine that would detect such cells and call it the “Indomitable.” In 1977, the first full body device with MR images was created.
What is it?
MRI assists in the diagnosing of various and potentially serious things. These can include brain, spinal cord, and liver. They also help with problems that may be associated with the female reproductive organs. The MRI will even find things like broken bones in the pelvis or joint issues that the X-Ray can not pick up. With the ability to see deep inside of the body, they can also detect places with bleeding or infections. Most often, they are used to identify tumors or small fractures that X-rays are unable to pick up.
How does it work?
MRI’s use a powerful magnet that is strong enough to produce a magnetic field that forces protons in the body. When a radio frequency current goes through the patient, the protons are stimulated which allows straining against the pull of the magnetic field out of the equilibrium, which strains against the pull of the overall magnetic field. When that specific field is turned off, the MRI has sensors that can detect the specific energy that is released. During this, the protons will realign with the magnetic field. The time and energy that this takes for the protons to realign and reg energy released depends on one thing. The environment and the overall chemical nature of the molecule. In short terms, it is an imaging procedure that uses magnets, radio waves, and a computer to see high resolution images of the inside of a body. In order to safely secure an image from the MRI scanner, the patient is placed on a table inside a large magnetic tube like object. The patient must remain completely still or the imaging process will be disrupted and the image will be blurred.The patient, on the table lies down, and the table then will slowly move into the MRI scanner. The Main magnet in the MRI creates a field that can be 1-4 thousand times stronger than earth’s magnetic field. They can last anywhere from 10 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the sole purpose of the scan.
Why was it invented?
Dr. Raymond Damadian had the unfortunate visual of the death of his grandmother from cancer. He witnessed her die a slow and painful death and knew he needed to do something to help. It was then he began his research and experimentation with the hope to create a machine that would be able to detect cancerous cells. To his surprise, he created the first full body scanner able to find dangerous cells.
“10 Facts About MRIs.” Medical Associates of Northwest Arkansas, September 24, 2015. https://www.mana.md/10-facts-about-mris/.
Staff, The Manual’s Editorial, By, The Manual’s Editorial Staff, and Last full review/revision June 2017 by The Manual’s Editorial Staff. “Quick Facts: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).” Merck Manuals Consumer Version. Accessed October 28, 2019. https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-special-subjects/common-imaging-tests/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri. “Invention of MRI.” Questions and Answers in MRI. Accessed December 1, 2019. https://mri-q.com/who-invented-mri.html.
Picture:
“Our Services.” test. Accessed October 28, 2019. https://www.sah.org.au/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri.
“Invention of MRI.” Questions and Answers in MRI. Accessed December 1, 2019. https://mri-q.com/who-invented-mri.html.
